Oral Health and Heart Disease
Your oral health is more important than you think. Not only does it affect your smile and your ability to eat and speak, but it can also have a significant impact on your overall health, including your heart health. Emerging evidence suggests that the state of your oral hygiene may have profound implications for the health of your heart. Individuals who suffer from poor oral health face an elevated risk of developing heart conditions, including heart attacks, strokes, or severe heart infections. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the connection between oral health and heart disease, shedding light on the importance of maintaining a healthy mouth to safeguard your heart.
1. Understanding the Link: Oral Health and Heart Disease
-
The Oral-Systemic Connection
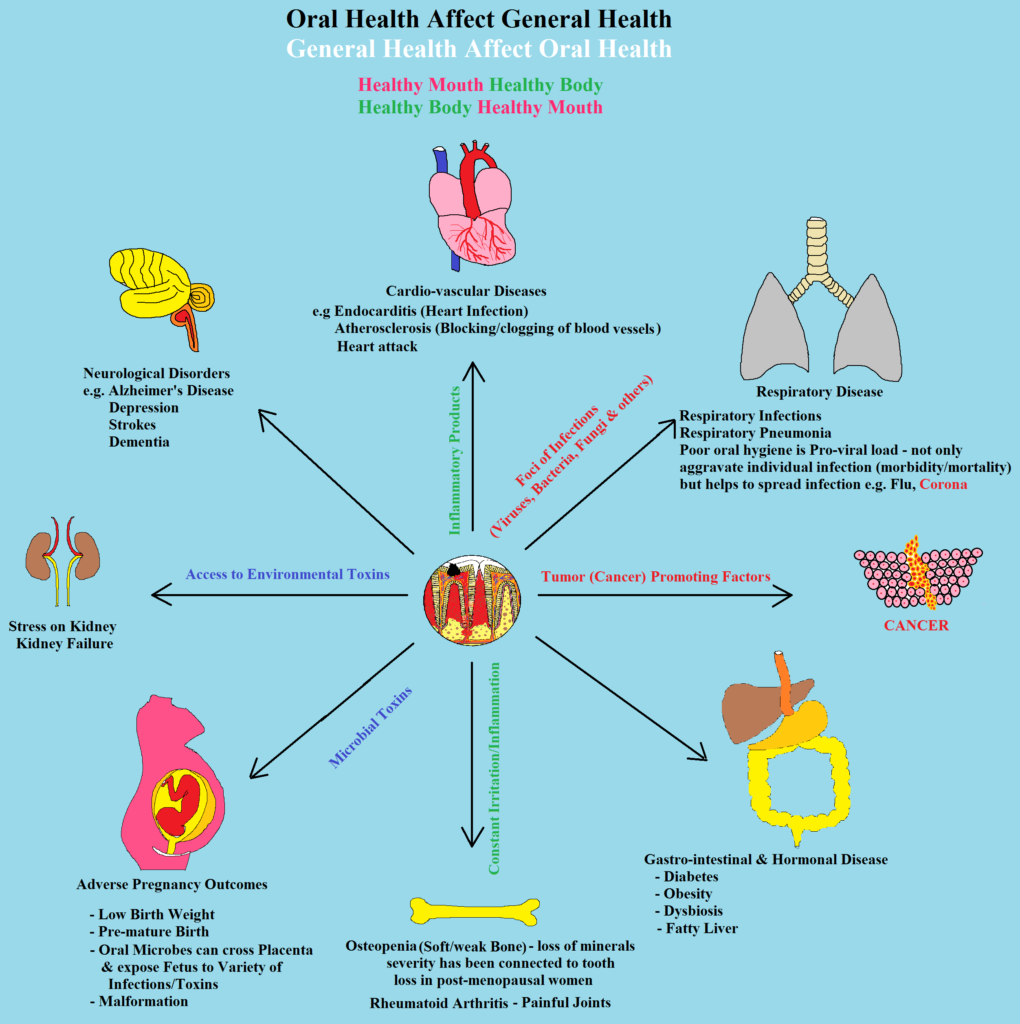
The connection between oral health and heart disease is part of a broader concept known as the oral-systemic connection. This idea suggests that the health of your mouth can have far-reaching effects on other systems in your body, including the cardiovascular system. It underscores the importance of viewing the body as an interconnected whole, where one aspect of health can influence another.
oral health impact on overall health
-
Inflammation: The Common Denominator
Inflammation is at the heart of the link between oral health and heart disease. Chronic inflammation in the gums, as seen in periodontal (gum) disease, can release inflammatory molecules into the bloodstream. These molecules can trigger inflammation in other parts of the body, including the arteries of the heart. Over time, this chronic inflammation can contribute to the development and progression of cardiovascular diseases.
2. The Role of Oral Bacteria
-
Gum Disease and Bacterial Spread
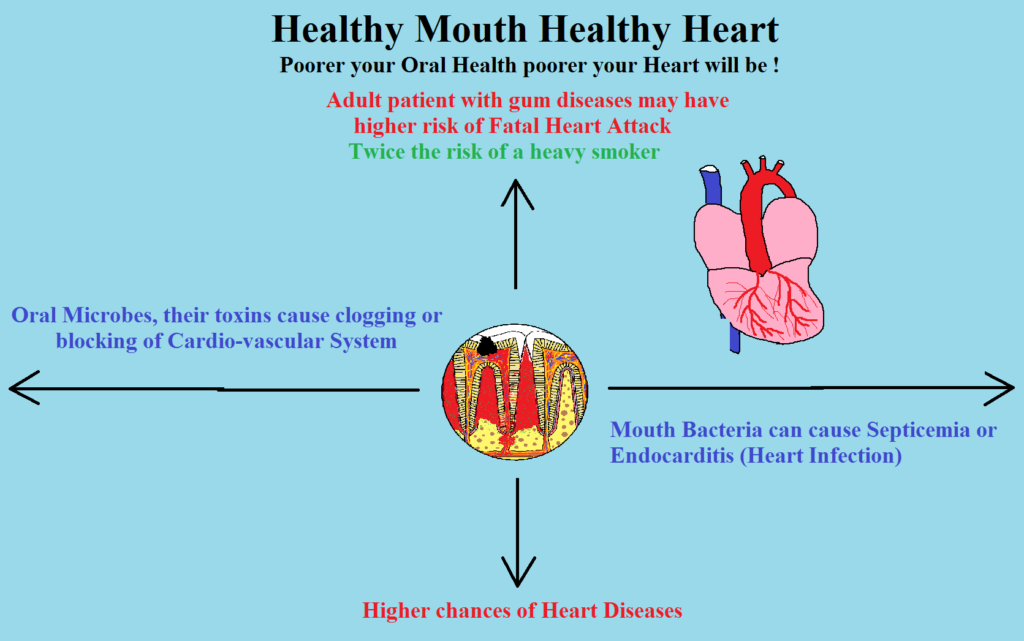
Gum disease, or periodontal disease, is a prevalent oral health issue characterized by the infection and inflammation of the gum tissues. The link to heart disease lies in the potential spread of harmful oral bacteria. As gum disease advances, bacteria can enter the bloodstream, creating a direct pathway to the heart and other vital organs. This can lead to systemic inflammation and the potential for cardiovascular complications.
-
The Path to Heart Complications
Once oral bacteria find their way to the heart, they can contribute to the formation of arterial plaque. Plaque buildup narrows the arteries and can lead to conditions such as atherosclerosis, which increases the risk of heart attacks and strokes. Additionally, oral bacteria can trigger an inflammatory response in the cardiovascular system, further elevating the risk of heart disease.
A study revealed that individuals with gum disease are at higher risk of developing heart diseases such as fatal heart attacks or strokes.
Oral health and heart diseases
3. Inflammation and Cardiovascular Risk
-
The Silent Culprit
Inflammation plays a pivotal role in the development of heart disease. The inflammation triggered by oral infections can contribute to atherosclerosis, where fatty deposits accumulate on arterial walls. This narrows the arteries, reducing blood flow to the heart and increasing the risk of heart attacks.
-
How Inflammation Affects Your Heart
Chronic inflammation not only contributes to atherosclerosis but can also destabilize arterial plaques, making them more likely to rupture. When a plaque ruptures, it can lead to the formation of blood clots that can block blood flow to the heart or brain, resulting in severe cardiovascular events.
4. Preventive Measures
-
Maintaining Oral Health
Proper oral hygiene practices are essential for preventing gum disease and reducing the risk of heart complications. This includes brushing your teeth at least twice a day, flossing daily, and correct use of an antimicrobial mouthwash. Regular dental check-ups and cleanings are also crucial for detecting and addressing oral health issues early.
-
Tips for a Heart-Healthy Mouth
In addition to daily oral care, maintaining a heart-healthy mouth involves controlling risk factors such as diabetes, high blood pressure, and smoking. Managing these conditions can help reduce the inflammation and bacterial load in your mouth, lowering the risk of heart disease.
5. The Importance of Regular Check-ups
-
Your Dentist as a Heart Health Ally
Your dentist plays a crucial role in your overall health. They can identify and treat gum disease and provide guidance on oral care practices tailored to your specific needs. Regular dental check-ups also offer an opportunity to discuss any concerns about your oral health’s impact on your heart.
-
Monitoring and Prevention
Regular dental visits allow for the monitoring of your oral health and the early detection of potential issues. By addressing oral health problems promptly, you can minimize the risk of systemic complications, including those related to heart disease.
Additional Tips for a Healthy Heart
Balanced Diet for Heart Health
- Strive for a balanced diet that includes moderate amounts of carbohydrates and fats, but avoid consuming both in excessive quantities simultaneously.
- Aim for a daily intake of a moderate amount of protein, ideally about 1 gram of protein per kilogram of body weight.
- Increase your consumption of fruits and vegetables to promote heart health.
- Be cautious of excessive intake of saturated and trans fats, sugar, and salt. Limit animal fats and use vegetable oils sparingly.
- Steer clear of highly processed or refined foods that contain excessive sugar, salt, unhealthy fats, and artificial additives whenever possible.
- Avoid regularly combining carbohydrates and fats in your meals. Opt for one or the other, with a preference for vegetable sources.
Moderation Is Key
- Keep in mind that moderation is the cornerstone of a healthy lifestyle. This applies to your diet, exercise, sleep, and overall lifestyle choices.
- Overindulging in even healthy foods or excessive exercise can have adverse effects on your body.
- Enjoy your favorite foods, but practice moderation and avoid consuming them daily.
Stay Hydrated
- Ensure you drink an adequate amount of water daily to support overall health, including heart health.
- Quality Sleep Matters
- Prioritize good sleep as it plays a vital role in heart health and overall well-being.
Moderate Exercise and Active Lifestyle
- Engage in moderate exercise regularly to keep your heart and body healthy.
- Avoid extended periods of sitting by incorporating light and continuous physical activity throughout your day.
- Consider daily walks or participating in sports you enjoy.
- Remember, consistency in activity is more beneficial than sporadic intense workouts. Strive for a balance of physical activity throughout the day.
Avoid Smoking
- Smoking is a major risk factor for heart disease. Quitting smoking or avoiding it altogether can significantly improve heart health. “Click here to read our article on quitting smoking or tobacco”.
Limit Alcohol Consumption
- Excessive alcohol consumption can lead to various heart-related issues. If you consume alcohol, do so in moderation.
Yoga and Meditation for Stress Management
- Chronic stress can negatively impact heart health. Incorporating practices like yoga and meditation into your routine can help reduce stress and promote heart well-being.
Conclusion
The link between oral health and heart disease is a fascinating and potentially life-saving area of study. Maintaining proper oral hygiene not only grants you a dazzling smile but also contributes significantly to your heart’s well-being. By embracing good oral health practices, controlling risk factors, and seeking regular dental care, you can significantly reduce the risk of heart disease and promote overall well-being. Remember, a healthy mouth can be a cornerstone of a healthy heart.
FAQs
Q1: Can poor oral health really affect my heart?
A1: Yes, there is growing evidence that poor oral health, especially gum disease, can increase the risk of heart disease. Inflammation and bacteria from oral infections can enter the bloodstream, potentially leading to cardiovascular complications.
Q2: How can I maintain good oral health?
A2: To maintain good oral health, brush and floss regularly, visit your dentist for check-ups and cleanings, and maintain a balanced diet. Avoid smoking and excessive alcohol consumption, as these can harm your oral and heart health. If you have any concerns about your oral health, be sure to talk to your dentist.
Q3: Are there any specific oral care tips for heart health?
A3: Yes, maintaining a heart-healthy mouth involves proper brushing and flossing techniques, regular dental check-up, and controlling risk factors such as diabetes and high blood pressure. Your dentist can provide personalized guidance.
Q4: How often should I see a dentist for heart health maintenance?
A4: Regular dental check-ups are recommended every six months. However, if you have specific oral health concerns or are at a higher risk of heart disease, your dentist may recommend more frequent visits.
Q5: Can treating gum disease improve heart health?
A5: Treating gum disease can reduce inflammation and the risk of bacterial entry into the bloodstream, which may contribute to improved heart health. It’s essential to consult both your dentist and healthcare provider for a comprehensive approach.
Q6: What are the symptoms of gum disease?
A6: The early signs of gum disease include red, swollen, and bleeding gums. As the disease progresses, you may also experience loose teeth, bad breath, and changes in your bite.