Dental Bridge Problems
Introduction
Dental bridges are a popular solution to replace missing teeth, offering both functional and aesthetic benefits. However, like any dental procedure, they are not without challenges. This article explores common dental bridge problems, their underlying causes, symptoms to watch out for, and how to manage or prevent them—making it your complete guide to bridge-related complications.
What Are Dental Bridge Problems?
A dental bridge is a fixed prosthetic used to replace one or more missing teeth by anchoring onto adjacent natural teeth or implants. While they restore oral function and appearance, they can present various problems over time due to poor oral hygiene, misfit design, wear and tear, or biological factors. Understanding these issues helps in early detection and effective management.
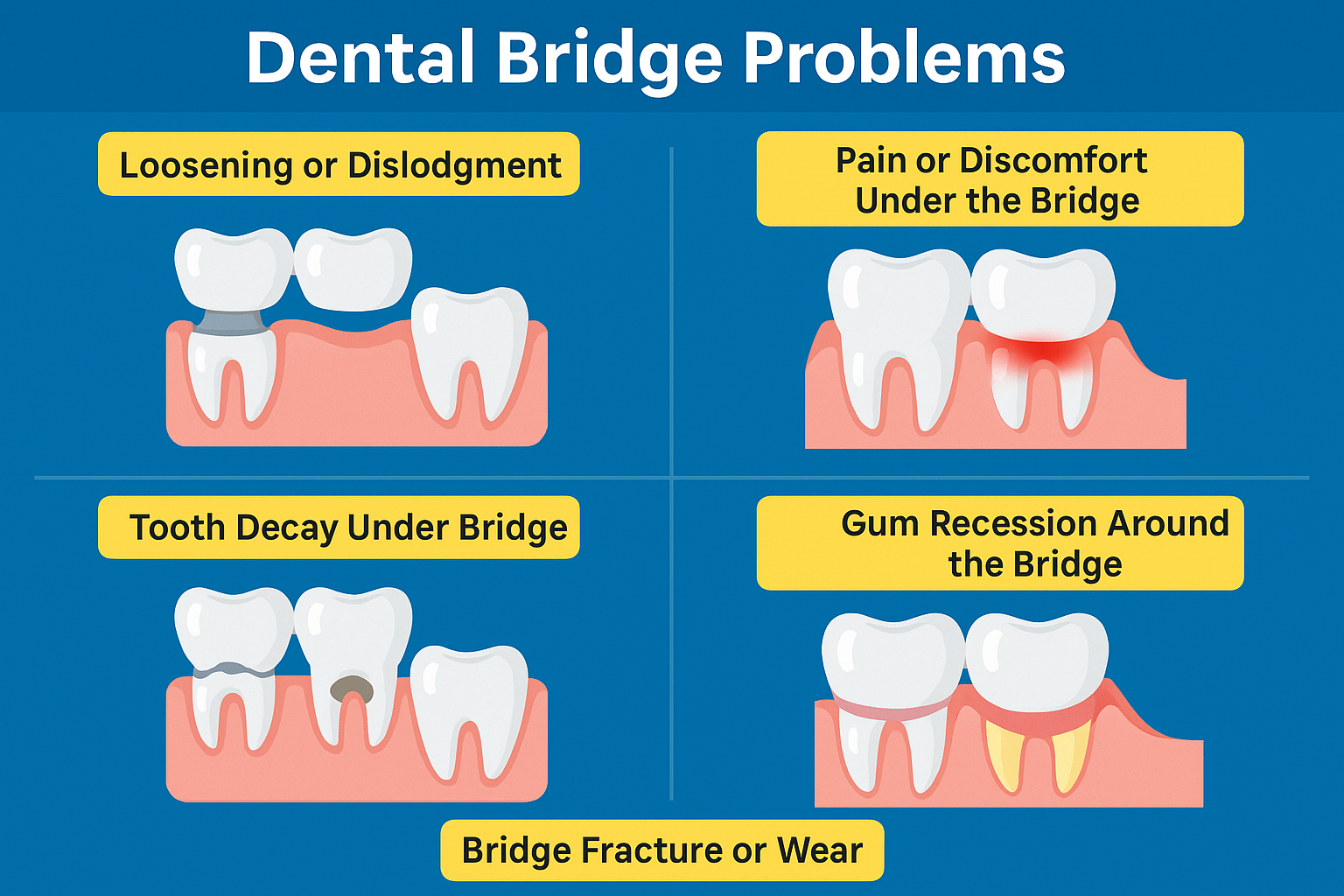
Common Dental Bridge Problems and Causes
- Loosening or Dislodgment
- Poor cementation or bonding
- Weak or damaged abutment teeth
- Bruxism (teeth grinding)
- Chewing hard foods
- Pain or Discomfort Under the Bridge
- Ill-fitting design causing gum irritation
- Decay or infection beneath the crown
- Residual root issues from previous dental work
- Tooth Decay Under Bridge
- Food and plaque accumulation under pontic and margins
- Poor oral hygiene habits
- Lack of flossing under the bridge
- Gum Recession Around the Bridge
- Aging or periodontal disease
- Poorly designed bridge pressing on gum tissue
- Inflammatory response from improper hygiene
- Bridge Fracture or Wear
- Material fatigue (especially in porcelain-fused-metal bridges)
- Chewing hard objects or foods
- Trauma or accidents
What Influences Dental Bridge Success and Failure?
Materials & Their Role in Bridge Longevity
- Porcelain: Prone to chipping, though aesthetically pleasing
- Metal: Durable but less natural-looking
- Zirconia: Strong and aesthetic, but expensive
Types of Bridges and Their Unique Challenges
- Traditional Bridges: Risk of affecting adjacent natural teeth
- Cantilever Bridges: Higher risk of loosening due to one-sided support
- Maryland Bridges: Risk of debonding due to minimal anchorage
- Implant-Supported Bridges: May face issues with implant failure or peri-implantitis
Cleaning & Hygiene-Related Issues
- Difficulty in cleaning under the pontic
- Risk of plaque retention leading to decay
- Need for floss threaders or water flossers
Bone Loss Under Pontic
- Lack of stimulation to jawbone under the missing tooth
- Long-term esthetic or functional impact
Symptoms Indicating Bridge Problems
- Bad breath or taste (indicating trapped food or decay)
- Bleeding or inflamed gums around the bridge
- Pain when chewing or biting
- Visible gaps between bridge and gum
- Loosening sensation or movement
Solutions and Remedies for Dental Bridge Problems
✅ Professional Dental Treatments
- Recementing or replacing the bridge
- Treating decay under the bridge
- Gum contouring or grafting for recession
- Replacing fractured prosthetic components
✅ Preventive Measures
- Daily brushing and flossing with floss threaders
- Regular use of antimicrobial mouthwash
- Dental visits every 6 months
- Periodic radiographic examination if advised
- Avoiding hard foods like ice or bones
- Use of interdental brushes to clean under the bridge
- Use of super-floss and floss threader
- Water flossers for hard-to-reach areas
- Avoid sticky, sugary snacks that promote decay
Conclusion
While dental bridges offer excellent restorative outcomes, being aware of dental bridge problems is essential to ensure their long-term success. By understanding the symptoms, causes, and preventive strategies, you can avoid most complications and enjoy the benefits of your dental bridge for years.
10 FAQs About Dental Bridge Problems
- Can dental bridge problems occur years after placement?
Yes, especially due to gum recession, decay, or material fatigue.
- How do I know if decay is forming under my bridge?
Symptoms include bad odor, discomfort, or visible darkening near the margins.
- What if food gets stuck under my bridge?
Use floss threaders or water flossers daily to remove trapped debris.
- Is it painful to fix a loose dental bridge?
Usually not, especially if it involves recementing. If decay is present, treatment may require local anesthesia.
- What is the average lifespan of a dental bridge?
Typically 5–15 years, depending on materials and oral hygiene.
- Can I switch from a bridge to implants later?
Yes, depending on bone availability and health status.
- Why do my gums hurt under the bridge?
Likely causes include irritation, poor fit, or trapped debris causing inflammation.
- How often should I get my dental bridge checked?
At least every 6 months during regular dental visits.
- Can a bridge affect my speech or chewing?
Initially yes, but most patients adapt quickly unless it’s ill-fitted.
- What happens if I ignore bridge problems?
It may lead to decay, gum disease, loss of supporting teeth, or complete failure of the bridge.

