Tooth sensitivity prevention and treatment
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on tooth sensitivity, where we delve into effective strategies for both prevention and relief. If you’ve ever experienced discomfort while indulging in your favourite hot or cold treats, you’re not alone. Tooth sensitivity can interrupt the simplest pleasures, but fear not – our guide is here to empower you with insights on how to prevent and find relief from this common dental concern. From practical tips on maintaining oral health to understanding the treatments that bring soothing relief, join us on a journey to conquer tooth sensitivity and regain your smile’s comfort. Let’s explore the world of “Tooth Sensitivity Prevention and Treatment” together.
What is Tooth Sensitivity?
Imagine enjoying your favourite ice cream or sipping a hot cup of coffee when suddenly, a sharp, fleeting pain disrupts the moment. This is a common experience for individuals with tooth sensitivity. It’s a condition characterized by a sudden twinge or discomfort in response to specific triggers like hot, cold, sweet, or acidic substances. This discomfort often stems from exposed dentin, the inner layer of the tooth that houses sensitive nerves.
Why Tooth Sensitivity Strikes?
Tooth sensitivity occurs when the tough outer layer of a tooth, known as enamel and cementum, wears down, revealing the nerves in the dentin or pulp beneath. Unlike enamel and cementum, these inner layers contain nerves, making the tooth sensitive to hot, cold, or sweet stimuli. The sensitivity can also result from damage to the tooth’s outer layer due to decay, fractures, worn or dislodged fillings, or gum disease, which exposes the nerves in the dentin or pulp, causing discomfort.
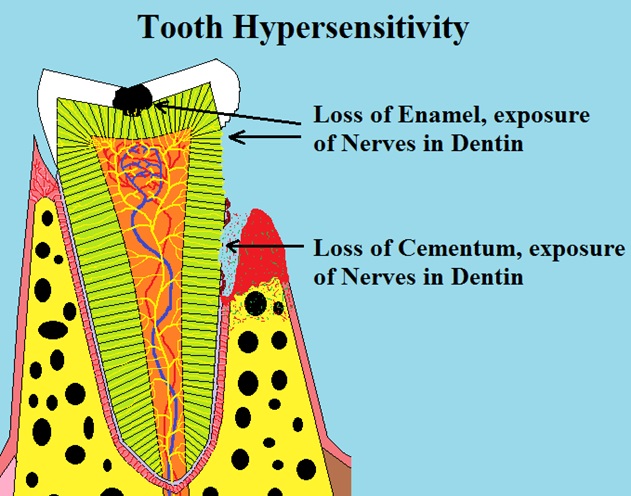
Damage to the Outer Layer Resulting in Exposure of Underlying Nerves
Causes of Tooth Sensitivity
Tooth sensitivity is a symptom, not a disease, often triggered by various dental issues. The following are the causes of tooth sensitivity:
- Impact of Brushing Habits: Aggressive brushing techniques and hard-bristled toothbrushes can wear down enamel and expose dentin.
- Receding Gums: Gum disease, tartar buildup, and misaligned teeth can lead to gum recession and heightened sensitivity.
- Outer Layer Erosion: Acidic foods, teeth whitening agents, improper dental habits, GERD, and systemic conditions can erode enamel and cementum.
- Tooth Decay: Cavities breach protective layers, exposing nerves and causing sensitivity.
- Bruxism (Teeth Grinding): Stress, neuromuscular issues, sleep disturbances, and medical conditions can contribute to grinding and sensitivity.
- Cracked or Chipped Teeth: Structural damage exposes sensitive inner layers.
- Dental Procedures: Certain treatments, like fillings or tooth whitening, may temporarily increase sensitivity.
- Worn Fillings and Damaged Crowns: Exposed dentin or pulp due to worn fillings or damaged crowns can lead to sensitivity.
Read in detail in our article where the causes of tooth sensitivity are revealed and explained.
Now, let’s delve into the heart of the matter – how to prevent and treat tooth sensitivity.
Prevention of Tooth Sensitivity
1. Embrace Proper Oral Hygiene
It all begins with a solid oral hygiene routine. Brush your teeth at least twice a day, using a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste. Floss daily to rid your teeth of plaque and prevent gum disease. Flossing your teeth daily is essential. It not only complements the work of your toothbrush but also reduces its workload. For a detailed guide on how to brush and floss correctly, refer to our article on brushing and flossing. A clean and healthy mouth is less prone to sensitivity. Remember, dental plaque is the most common trigger factor for initiating sensitivity, aside from exposure to cold and hot drinks and acidic foods.
2. Choosing the Right Oral Hygiene Aids and Techniques
When it comes to preventing tooth sensitivity, opting for a soft-bristled toothbrush is a smart move. Not only does it protect your enamel, but using gentle, circular brushing motions is more effective and less harsh than vigorous horizontal strokes.
- Avoid aggressive brushing habits – those long horizontal strokes may seem efficient, but a gentle and correct brushing technique is the way to go. Remember, once your tooth is damaged, it can’t repair or regenerate itself like other tissues in your body.
- For your daily dental routine, consider an ultra-soft or soft-bristled toothbrush paired with fluoride toothpaste. If you’re into technology, an electric toothbrush is a fantastic choice. It applies minimal pressure on your teeth and gums, ensuring a thorough yet gentle clean.
- Here’s a golden rule: don’t unnecessarily over-brush areas that are already clean or easily cleansable. It’s about efficiency, not excess.
- When it comes to toothpaste, choose a low-abrasive option with a low RDA (Relative Dentin Abrasivity). Avoid using abrasive tooth powders or teeth whitening products regularly, as they can be harsh on your enamel.
- Taking these simple steps in choosing the right oral hygiene aids and techniques ensures you’re giving your smile the care it deserves – gentle, effective, and essential for preventing tooth sensitivity.
3. Preventing Tooth Wear and Erosion: Preserving Your Dental Health
Tooth wear and erosion can lead to increased tooth sensitivity, affecting your oral health and overall well-being. Implementing preventive measures is crucial in maintaining strong and healthy teeth. Here are essential strategies to minimize tooth wear and erosion:
Maintain a Balanced Diet:
- Consume acidic foods and beverages in moderation, as they contribute to tooth erosion.
- Include calcium-rich foods like dairy products to promote enamel strength.
- Brush your teeth twice daily with a fluoride toothpaste.
- Use a soft-bristled toothbrush to avoid abrasive damage to tooth surfaces.
- Implement gentle brushing techniques to prevent enamel erosion.
Choose the Right Toothbrush and Toothpaste:
- Opt for a toothbrush with soft bristles to prevent abrasive damage.
- Select a toothpaste designed for sensitive teeth, containing fluoride for outer layer protection.
Stay Hydrated:
- Drink plenty of water throughout the day to help neutralize acids in the mouth.
- Rinse your mouth with water after consuming acidic foods or beverages.
- Refrain from brushing your teeth immediately after consuming acidic foods and beverages, as doing so can further damage the outer layer of your teeth.
Manage Acidic Substances Wisely:
- Reduce intake of acidic drinks like sodas, citrus juices, and sports drinks.
- Be cautious with acidic fruits, such as lemons and oranges.
- When consuming juice from acidic fruits, use a straw to minimize direct contact with teeth, reducing the potential for damage.
Prevent Acid Erosion from Various Sources:
- Manage acid regurgitation, GERD, and anorexia nervosa through medical intervention and lifestyle adjustments.
- Address systemic conditions that may contribute to acid erosion. During morning sickness in pregnancy, consider using fluoride mouthwash or rinsing the mouth with water to neutralize acids and protect teeth.
By incorporating these preventive measures into your daily routine, you can significantly reduce the risk of tooth wear and erosion, ensuring a healthy and resilient smile.
Avoid DIY Treatments:
- Refrain from using self-made treatments, such as homemade products or commercial products claiming rapid results, without consulting professionals.
- Exercise caution with products like teeth-whitening pastes, strips or bleaching promising results in short-time, or excessively abrasive toothpaste for achieving shiny teeth. Consult with dental professionals before trying such treatments.
Preventive Measures for Cracked or Chipped Teeth:
- Avoid biting hard objects like ice or non-food items to reduce the risk of structural damage.
- Consider using a mouthguard, especially for sportspersons or professionals, during activities that pose a risk of trauma to the teeth, such as playing contact sports.
- Schedule regular dental check-ups to identify and address potential issues early on, preventing the progression of cracks or chips.
4. Regular Dental Check-ups
- Routine dental check-ups are not just about cleanings; they are your frontline defence against potential dental issues.
- Your dentist can identify signs of sensitivity and address them before they become more problematic.
Treatment of Tooth Sensitivity
Identify the Root Cause
- Schedule a comprehensive dental check-up with your dentist to pinpoint the underlying cause of tooth sensitivity.
- Discuss your symptoms and dental history to facilitate an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan.
Addressing Dental Issues
- Address any existing dental problems, such as cavities or gum disease, to prevent their exacerbation and reduce sensitivity.
- In cases where structural issues are contributing to sensitivity, dental procedures like bonding, inlays, or crowns may be recommended to address these concerns.
- Seek treatment for misaligned teeth to address issues such as gum disease, gum recession, and teeth abrasion due to abnormal contacts, as they can cause tooth sensitivity.
- Gum grafts may be recommended to cover exposed roots in cases of receded gums, preventing sensitivity. For high frenum attachment, a frenectomy may be necessary to prevent further gum recession.
- Obtain dental treatment for worn fillings and damaged crowns, as exposed dentin or pulp resulting from these issues can lead to sensitivity.
- The treatment for bruxism typically involves the use of a nightguard to minimize teeth grinding and protect against sleep-related dental damage. Additionally, incorporating meditation and yoga can help alleviate stress, a common contributing factor to bruxism.
Professional Desensitizing Treatments
Tailored for immediate and lasting relief, professional desensitizing treatments, administered by skilled dental practitioners, target specific tooth sensitivities, enhancing overall well-being. Explore key interventions below:
- Fluoride application: Applying fluoride helps strengthen tooth enamel, reducing sensitivity by protecting against acid erosion.
- Laser therapy: Laser treatments can address sensitivity by sealing open dentinal tubules and promoting tissue regeneration, providing relief for patients with chronic sensitivity.
- Dental bondings: Bonding involves applying a tooth-colored resin to exposed dentin, effectively covering sensitive areas and enhancing tooth protection.
- In-office desensitizing treatments: Dentists can perform procedures like fluoride varnish or resin infiltration to alleviate sensitivity during a dental visit.
- Nerve desensitization treatments: Specific treatments target nerve pathways to reduce sensitivity and improve comfort for individuals with chronic dental pain.
- Dental sealants: Applying sealants to the tooth surface forms a protective barrier, reducing sensitivity by shielding against external stimuli like temperature changes.
Customized Oral Care Regimen
- Work with your dentist to develop a personalized oral care routine, including the use of desensitizing toothpaste and mouthwash.
- By taking a proactive approach and collaborating with your dentist, you can effectively manage and alleviate tooth sensitivity.
Harness the Power of Desensitizing Toothpaste
Your dentist might prescribe a high-fluoride or desensitizing toothpaste for at-home use. This specialized toothpaste provides an additional layer of protection over exposed dentin and can lead to significant reduction over time.
How to Use Desensitizing Toothpaste
Select an Ultra-Soft Toothbrush:
Choose an ultra-soft toothbrush to minimize abrasion and reduce potential irritation.
Apply Desensitizing Toothpaste:
Brush your teeth with desensitizing toothpaste, ensuring coverage over sensitive areas.
Avoid Immediate Rinsing:
- Refrain from rinsing immediately after brushing to allow the toothpaste ingredients to interact and form a protective barrier over exposed nerve endings.
- Wait for a minimum of 5-10 minutes before rinsing or consuming food and beverages to ensure optimal effectiveness.
Consider Desensitizing Mouthrinses:
Supplement your oral care routine by using desensitizing or fluoride mouthrinses in conjunction with desensitizing toothpaste because they can reach areas where paste cannot.
Frequency of Use:
Use the desensitizing toothpaste at least 2-3 times daily, adjusting the frequency based on your level of sensitivity.
Continue for Few Weeks:
Maintain this routine for at least few weeks to allow sufficient time for the desensitizing agents to take effect.
Monitor Sensitivity:
Assess the reduction in sensitivity over time. If sensitivity persists, consult your dentist for further guidance.
By following these steps and maintaining regular communication with your dentist, you can optimize the effectiveness of desensitizing toothpaste in managing tooth sensitivity.
Transitioning After Sensitivity Relief
Once tooth sensitivity has resolved, it is generally not necessary to continue using desensitizing toothpaste. Desensitizing toothpaste can be costlier than standard fluoride toothpaste, and as sensitivity diminishes, you can return to your routine fluoride toothpaste. However, it remains essential to maintain good oral hygiene practices.
Reverting to Fluoride Toothpaste
Shift back to your regular fluoride toothpaste once sensitivity has been effectively addressed.
Cost Considerations
Recognize that desensitizing toothpaste can be more expensive, and adjusting to a standard fluoride toothpaste can be a cost-effective choice.
Sustaining Oral Hygiene
Despite the transition, continue to uphold strong oral hygiene practices, including regular brushing, flossing, and routine dental check-ups.
By adapting your oral care routine based on the resolution of sensitivity and cost considerations, you can strike a balance between effective dental care and economic practicality.
Medical Consultation
Reach out to your physician and psychiatrist if experiencing frequent vomiting and acid regurgitation, especially in cases related to anorexia nervosa, bulimia, and GERD.
Stress Management Through Mind-Body Practices
- Embrace stress-reducing activities such as yoga and meditation.
- These practices not only calm the mind but also contribute to preventing teeth grinding and controlling acid regurgitation disorders.
By prioritizing a holistic approach to health, including both physical and mental well-being, you contribute to the preservation of your oral health and overall quality of life.
Conclusion
Understanding the causes, prevention, and treatment options for tooth sensitivity empowers individuals to take proactive steps in maintaining optimal oral health. Remember, regular dental care, a thoughtful oral hygiene routine, and open communication with your dentist are key elements in preventing and addressing tooth sensitivity effectively.
Addressing tooth sensitivity solely with desensitizing toothpaste at home may provide temporary relief but doesn’t prevent the underlying issues. Sensitivity is like a signal, indicating potential problems like decay, tooth wear, or gum diseases. Seeking advice from your dentist is crucial as they can identify and treat the root cause rather than just relieving symptoms. Remember, sensitivity is both preventable and treatable, and consulting a professional ensures a personalized approach to tackle it at its source, promoting long-term oral health.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: Can tooth sensitivity be completely cured?
A: The extent to which tooth sensitivity can be cured depends on the underlying cause. While some cases can be effectively treated, others may require ongoing management and lifestyle adjustments.
Q: Can I use over-the-counter desensitizing toothpaste?
A: Yes, over-the-counter desensitizing toothpaste can be an effective solution for mild tooth sensitivity. However, it’s advisable to consult your dentist for personalized recommendations based on your specific situation.
Q: Are there lifestyle changes to help prevent tooth sensitivity?
A: Absolutely. Adopting a tooth-friendly diet, managing stress, avoiding excessive teeth grinding, and maintaining good oral hygiene are crucial lifestyle changes that can significantly contribute to preventing tooth sensitivity.