
dental specialties
Introduction
The modern refined (soft and sticky) sugary diet has not only worsened our oral but systemic health too. The mouth has the second largest and most diverse microbiota after the gut and it became a constant source of inflammation. Tooth decay and gum diseases are one of the most common diseases affecting mankind. Teeth, gums, jaws, salivary glands, and oral-facial structures are interconnected complex members of the same family. Dentistry is not just limited to teeth. As everyone is a dental patient, dentists routinely encounter medical conditions. Many systemic diseases usually manifest in the oral cavity. Furthermore, dental tissues once damaged cannot be regenerated or repaired by themselves. Dentists have to be both doctors as well as engineers. You need special skills and knowledge about dentistry, medicine as well as engineering to manage dento-maxillofacial structure. Oral health is necessary to maintain your overall health and well-being. That’s why, dentistry demands extensive, time-consuming, rigorous training to master its art and science. Dental specialties are developed to improve the art and science of dentistry and the quality of patient care. Many patients are not familiar with dental specialties/specialists. As of this writing, there are twelve dental specialties / dental specialists. It is important for you to know about dental specialties, what they do, and which specialist is BEST for you.
Study Programs in Dentistry
Dentistry, in the field of study, offers both graduate (bachelor’s) and post-graduate (master’s) degree programs. A bachelor’s degree known as a Bachelor of Dental Surgery (BDS) or a Doctor of Dental Medicine (DMD), is a four-year study program that provides basic knowledge and practical skills in the field of oral health so that you can apply the same to diagnose and treat the patients of this field in an optimal way, as well as to educate people about preventive measures. Upon completion, graduates are eligible to practice general dentistry.
Master of Dental Surgery (MDS) is a post-graduate degree program in dentistry that take three years to complete. Individuals must have completed BDS to be eligible for the MDS program. MDS is a dental specialization course that focuses on the advanced study of a particular area of dentistry, much like a cardiologist or neurologist. MDS course takes three years to complete and includes coursework, clinical training, and research. Upon completion, post-graduates are eligible to practice as a specialist in their field as well as general dentistry.
In some countries that recognize dental specialties, the specialist is only allowed to practice the specialty and cannot carry out the practice of general dentistry. A general dentist may refer patients (complex cases), and a specialist’s practice is mainly on a referral basis. In some countries, a specialist can conduct general as well as specialty practice.
12 Dental Specialties include:
Oral Medicine and Radiology
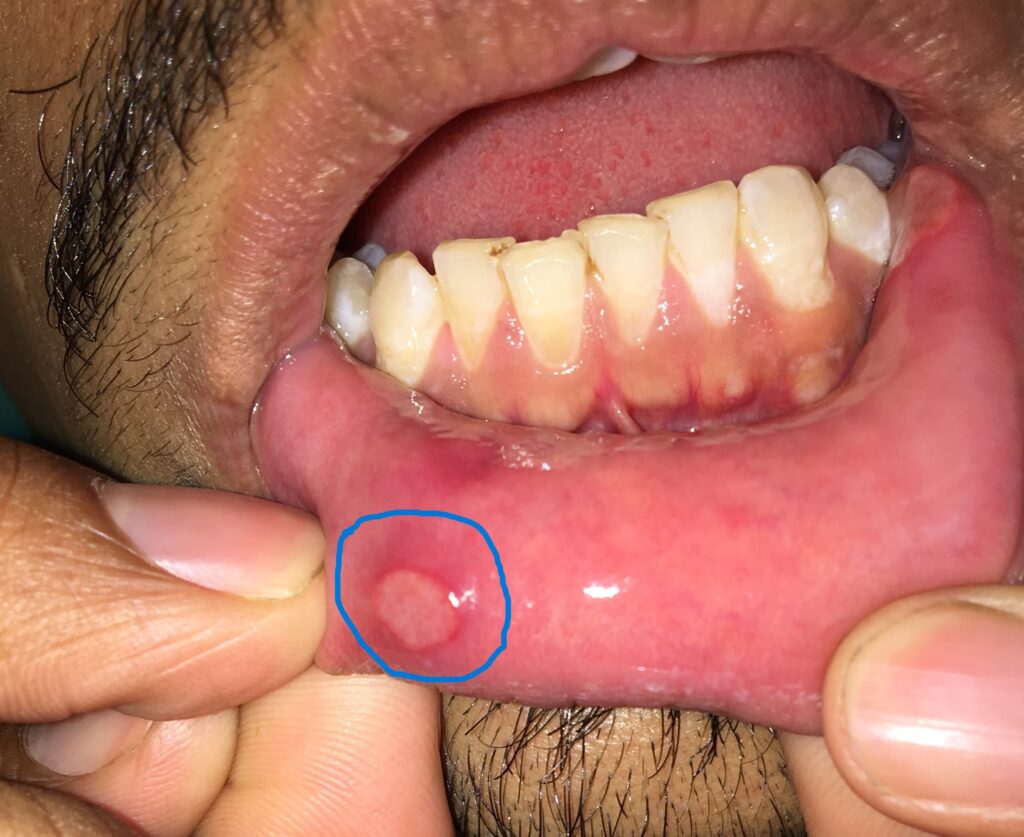
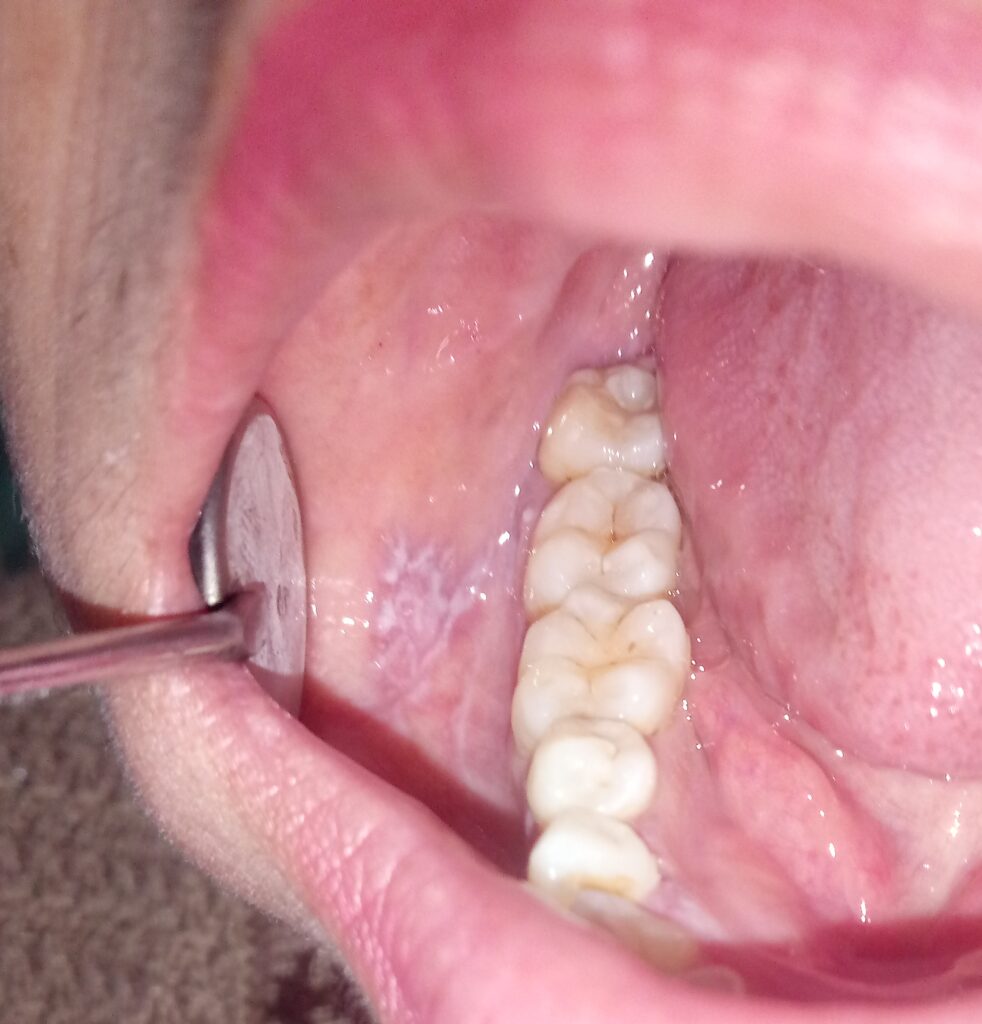
Oral Medicine and Radiology specialist is also called an oral physician. He/she does a comprehensive analysis and tries to find out all your dental, orofacial, and medical problems, and then he/she treats or refers you to your respective dental or medical specialist for treatment.
Services:
- The oral physician is the best one to diagnose (detect) all your dental-oral-facial diseases, and make a comprehensive treatment plan that not just addresses your oral but systemic problems too.
- Diagnosis (detection) and medicinal treatment of teeth, mouth, jaws, and oro-facial diseases, including oral precancer.
- Detection of oral cancer and precancer. We recommend you first consult your oral physician if you have any patch or ulcer in your mouth.
- Dental management of medically compromised patients.
- An oral physician can identify systemic (body) diseases from a patient’s oral picture.
- Minor surgical procedures such as removal of precancer patches or other oral lesions, and taking biopsies for confirmatory diagnosis.
- Laser therapy for pre-cancerous patches and other oral lesions.
- Management of jaw-joint (TMJ) related problems.
- Production and interpretation of X-ray images of teeth, mouth, face, and jaws. The best doctor who can interpret X-ray images of your teeth and jaws is your oral radiologist.
- Assessment and identification of relevant medico-legal / forensic cases through clinical and X-ray examinations.
The oral physician has professional experience in all aspects of subjects i.e., dentistry, medicine, and radiology. He/she can better communicate with medical specialists to clear the patient for dental surgical procedures to avoid untoward complications.
Periodontics
Periodontics is the specialty of dentistry that encompasses the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of diseases affecting the gums and supporting structures (bones) of the teeth, whether they are natural or manmade teeth. The specialist of this branch is called a Periodontist (Gum specialist). Gum disease is one of the most common diseases of mankind. If it is neglected or left untreated can lead to tooth loss. It is a major cause of tooth loss in adults.
Services:
- Periodontists guide you about how to prevent gum diseases. They also guide you about the oral hygiene aids (toothbrushes, flosses, interdental brushes, etc.) required and how to use them.
- Treatment of simple as well as complex cases of gum diseases.
- Scaling and root planning (teeth cleaning) – it means removal of tarter and plaque from between teeth and gums. It also includes the removal of external stains e.g., tobacco, and coffee stains present on your teeth.
- Gum surgeries and regenerative procedures to restore your gum health and aesthetics.
- Plastic surgeries to treat your receded gums or exposed root (long tooth).
- Surgical correction of abnormal frenum and vestibules of mouth because abnormal one pulls your gums down.
- Make a short-looking tooth long by cutting its gums (crown lengthening).
- Laser surgeries to remove bumps or growths on your gums.
- Dental implant and in its care. Remember, post-operative care of dental implants is more important than just the placement of implants.
Orthodontics
Orthodontics is the dental specialty that focuses on the diagnosis, prevention, interception, and treatment of crooked teeth (bad bites), jaws, and faces. An Orthodontist does teeth straightening by moving them through jaw bones with the use of braces and other corrective appliances. Crooked (misaligned) dentofacial structures can affect your chewing, speech, and facial appearance as well as your oral and general health. It can also influence your psychological health, particularly in children and teenagers who are always teased. Some people with crooked teeth feel less attractive or less confident. They never open up. It may affect their personality and life on a day-to-day basis. Treatment depends on how severe the misalignment is, how it affects you and how you deal with it.
Services:
- Orthodontists can guide you on how to prevent misalignment of teeth, jaws, and face.
- Preventive functional therapy in children (during growth).
- Straighten your crooked teeth, jaws, and face.
- Correct your bad bites and occlusion (how teeth come in contact with each other).
- In some cases, orthognathic (jaw-straightening) surgery may be required where jaw growth has been completed. In such cases, orthodontists do orthodontic (teeth straightening) treatment while oral and maxillofacial surgeons do orthognathic (jaw straightening) surgery that provides maximum benefits to both patients as well treating doctors. However, braces can successfully treat patients of any age.
Pedodontics
Pedodontics is a specialty of dentistry that deals with the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of dental problems in children and infants.
Services:
- Pedodontist not only deal with your children’s teeth but their overall health and development.
- They can guide you about dental preventive measures required even before the birth of your child.
- Habit-breaking therapy to stop bad habits such as thumb sucking, tongue thrusting, mouth breathing, etc. Such habits if left untreated can adversely affect the growth and development of your child’s teeth, jaws and face.
- Pedodontists either work independently or with an orthodontist to carry out preventive functional therapies in children to prevent misalignment of teeth, jaws, and face.
- Preventive treatments such as fluoride applications, timely removal of milk teeth, or space maintainer for the smoother eruption of adult teeth.
- Dental treatments – fillings, root canals, extraction, cleaning, and tooth replantation.
- Administer conscious sedation to uncooperative children or children with dental phobias.
- Dental treatment for children with special abilities.
- Communicate and work with multiple medical and dental specialists to manage children with complex problems e.g., cleft lip and palate, a child with the syndrome (multiple malformations) to improve the child’s overall health and development.
Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery (OMFS)
It is a major surgical specialty that deals with the diagnosis and surgical treatment of diseases, disorders, injuries, and defects of teeth, mouth, jaws, face, and neck.
Services:
- Administer safe and effective local anesthesia. In some countries, oral and maxillofacial surgeons are trained to administer general (whole body) anesthesia or deep sedation.
- Simple and complex extractions of teeth.
- Surgical treatment of head and neck infections.
- Surgical placement of simple as well as complex dental implants.
- Surgical treatment of cysts, tumors, and oral cancers.
- Surgical treatment of dentofacial fractures.
- Reconstructive surgery to rebuild dento-orofacial structure damaged by injury or diseases.
- Orthognathic surgery (jaw straightening surgery) in cases of misaligned teeth and jaws.
- Plastic surgeries to improve your oral and facial appearance.
Endodontics
Endodontics is a dental specialty centered on preventing, diagnosing, and treating diseases and conditions affecting the tooth pulp, such as tooth decay, wear, and injuries in adults. The primary objective is to preserve teeth by employing procedures like restorations, root canal treatments (RCTs) and pulp vitality-preserving methods. Endodontists aim to save teeth whenever possible, ensuring the patient’s oral health and function.
“Endo” means “inside” and “dontic” refers to “tooth”. It is a department of restoration and root canal treatments. If a decayed tooth is left untreated could result in tooth loss. Endodontists’ motto is to save the tooth either by restoration or by root canal.
Services:
- Administer safe and effective local anesthesia for painless restorative procedures.
- Treatment of decay/cavity, fractures, wear, and other defects in adult teeth that includes restorations (fillings), root canal treatments (RCT), and crowns or veneers (partial crowns).
- Tooth replantation (when the tooth came out after injury) in adult patients.
- Preventive measures like fluoride applications and pit and fissure sealants.
- Teeth-bleaching (whitening) in case of inner stains.
Prosthodontics
This branch deals with the replacement of lost teeth and jaw structures by constructing prostheses (implants, crowns, bridges, dentures, and dento-maxillofacial prostheses) to improve aesthetics and function. The term “prostho” means “replacement” and “dontic” refers to “tooth”. Dental prostheses are either fixed or removable. They are supported or fixed on adjacent natural teeth or dental implants. Prostheses are made up of either acrylic or metals or porcelain or ceramics or their combination.
Diseases, injuries, infections, cancers, and surgeries usually result in the loss of teeth and associated facial tissues including eyes and ears. These lost structures are replaced with prostheses. Hence, the specialist in this branch is known as an Oral and Maxillofacial Prosthodontist. They not only restore your function and smile but rebuild your confidence.
Services:
- Dentures – Dentures consist of artificial teeth attached to a pink or gum-colored plastic base. The denture can be either a full denture (used to replace all teeth) or a partial denture (used to replace some teeth). Dentures are an either removable or fixed type.
- Fixed Bridges – Dental bridges fill the gap created by one or more missing teeth.
- Crown (cap) – A patient needs an artificial crown, when a large portion (around 2/3rd) of the crown of the natural tooth has been lost or compromised and, the tooth cannot be restored just by a filling. The natural crown is a visible part of any tooth above the gum line. An artificial crown is also necessary after RCT to strengthen the weakened tooth to prevent its fracture.
- Partial crown (Veneer) – a wafer-thin shell of ceramic that covers only the front (visible) surface of the tooth.
- Maxillofacial Prostheses – Artificial replacement of lost part of jaws or face after cancer, injury, infection or surgery, or in case of any congenital or acquired defects to improve functions and aesthetics of an individual.
- Prostheses to treat other oro-facial disorders – Prosthodontists also make bite plates, mouth guards, jaw repositioning devices, and anti-snore devices. They work with other medical and dental specialists to treat teeth clenching, bruxism (teeth-grinding), TMJ (jaw joint) disorders, snoring and obstructive sleep apnea (OSA).
Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology
Oral and maxillofacial pathology is the specialty of dentistry and discipline of pathology which deals with the microscopic study of diseases and conditions affecting the oral and maxillofacial region.
Services:
- Oral and Maxillofacial pathologists give the final confirmation of the diagnosis of orofacial diseases, including oral cancer by examining a piece of diseased tissue under the microscope (Biopsy). The biopsy is considered as the “Gold Standard” of diagnosis in Medicine. Diagnosis is very important in deciding the treatment plan. The correct diagnosis can prevent complications and save lives. In most diseases, a biopsy (microscopic examination) is the only way of definitive diagnosis.
- They examine and provide a microscopic diagnosis of the biopsied tissue sent to them by a dental or a medical specialist.
- A biopsy is a sample or a small piece of tissue taken from the body or diseased organ in order to examine it under a microscope to find out the definitive diagnosis.
- Microscopic assessment and identification of medico-legal / forensic cases through clinical and radiological examinations.
Public Health Dentistry
This branch deals with preventing and controlling dental diseases and promoting dental health through organized community efforts.
Services:
- Dental public health specialist works with local and national Government to develop oral health policies, programs, and services for the community. Basically, they help to prevent and control dental and oral diseases and promote oral health through organized community efforts.
- They are involved in the assessment of oral health needs and improving the oral health of the population rather than individuals.
Other specialties
In some countries, the following branches are recognized as separate specialties of dentistry.
General Dentistry
A general dentist is your primary dental care provider. He/she takes care of most of your dental needs, which may include dental examinations, X-rays, scaling, fillings, RCTs, extractions, crowns, veneers, bridges, dentures, and preventive care. A general dentist can perform most of the same procedures a specialist performs. However, there may be a time when your general dentist will refer you to a specialist. The reason could be the complexity of a procedure, the patient’s health, or because you feel your procedure warrants a specialist. Whatever the case may be, we recommend consulting with your general dentist first, and then, if necessary, with your referred dental specialist. So, who are the specialists? A specialist is a general dentist who has taken additional extensive training in any one branch of dentistry. However, a specialist is a general dentist first, and then a specialist. They focus primarily on performing specific procedures pertaining to that branch. An experienced specialist is the best doctor in his specialty.
Forensic Dentistry
It is a specialty of dentistry and the discipline of Forensic Medicine and, in the interest of justice that deals with the identification and presentation of dental evidence in a court of law.
Enamel (the outer layer on crowns of teeth) is the hardest structure in our body and is very much stronger than our bones. Human teeth are the most indestructible organ and can withstand the test of time and temperature because of their highly resistant composition. They can survive not only after death but remain unchanged for thousands of years. A well-known example is the teeth found in the mandible of a Tabun man aged about 35,000 years old.1 Teeth are frequently the only DNA source available for identifying mutilated human remains. The unique composition of teeth provides additional protection to DNA compared to bones making them the preferred source of DNA in many cases. Interestingly, the treatment given by the dentist (fillings, crowns, dentures, or implants) is itself the biggest uniqueness for an individual and the key in the identification.
Services:
- Identification of found human remains.
- Identification of unknown body from dental records.
- Identification of mass fatalities in disaster.
- Assessment of bite mark injuries.
- Identification of victim as well as criminal.
- Assessment of abuse cases.
- Age determination of a living as well as a deceased individual.
- Sex determination of remains.
- Assessing dental injuries in medico-legal cases.
- They also assist in studying the lifestyle and diet of primitive people from dental findings at an archaeological site. Forensic studies also help in understanding evolution.
Implant Dentistry
A dental implant is nothing but a fixed prosthesis. A metal screw is placed into your jawbone where the tooth is missing and an artificial crown (tooth) is placed on top of it. A dental implant act like the root of a natural tooth. You can have just one implant or a full set to replace all your teeth. Dental implants have many benefits over traditional removable dentures as well as natural teeth-supported fixed bridges. A specialist in dental implants is called a Dental Implantologist.
Services:
- Single tooth replacement.
- Multiple teeth replacement.
- Implant-supported fixed bridges.
- Implant-supported fixed dentures.
- A dental implantologist also provides solutions for patients who have severe bone loss in their jaws and cant be treated with traditional prostheses.
Dental Sleep Medicine
Dental sleep medicine is a branch of dentistry that focuses on the diagnosis and treatment of sleep-related breathing disorders, such as snoring and sleep apnea (SA). SA is a serious medical condition in which breathing repeatedly stops and starts during sleep. It can lead to a number of health problems, including high blood pressure, heart disease, stroke, and diabetes.
Services:
- Dental sleep medicine dentists use oral appliance therapy to treat SA. Oral appliances are custom-made mouthpieces that patients wear during sleep. The appliances work by positioning the lower jaw forward, which helps to keep the airway open.
- By collaborating with physicians, dental sleep medicine dentists can provide patients with customized solutions that improve their sleep quality and overall well-being.
Dental Ancillaries
Dental Hygienist
Dental hygienists assist dentists or dental specialists by conducting periodic preventive periodontal (gums) cleaning and advising patients on oral hygiene and care. A dental hygienist is an oral healthcare professional who specializes in cleaning, scaling, and polishing teeth under the supervision of a dentist or a dental specialist.
Dental Mechanics
Dental mechanics make dentures, crowns, bridges, braces, and other dental devices prescribed by a dentist or a dental specialist. The dental mechanics’ program teaches you the skill required to fabricate dental prostheses and devices.
Dental Assistant
A dental assistant helps dentists or dental specialists in all possible ways, which enables the dentist to provide efficient, high-quality care to patients. They work under the supervision of dentists.
A dental assistant typically does the following tasks:
- Sterilizing dental instruments
- Pre-operative preparation
- He/she assists the dentist or a specialist with dental procedures, such as fillings, extractions, etc.
- Process X-rays and lab tasks such as pouring dental impressions, making casts, etc.
- Handling administrative tasks such as billing, appointments, treatment records, etc.
References
- Whittaker DK. Introduction to forensic odontology. Quintessence Int. 1994; 25: 723–30.









Pretty nice post. I just stumbled upon your blog and wanted to say that I’ve reallyenjoyed surfing around your blog posts. In any case Iwill be subscribing to your rss feed and I hope you write again soon!
Thanks a lot for your encouragement, please share if you think it is useful for others, thank you
Your article helped me a lot. what do you think? I want to share your article to my website: gate io
Thanks a lot for your encouragement, please share it, thank you