Introduction
Why dentistry is a separate course rather than a specialization after medical school is a question that often arises. Dentistry, as a distinct branch of medicine, focuses on the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of diseases and conditions related to teeth, gums, jaws, and oral-facial structures. While medicine has various specializations like ENT, Orthopedics, and Ophthalmology, dentistry stands apart as more than just a medical specialty. In this blog, we delve into the reasons why dentistry is a separate course and explore the unique aspects that set it apart from traditional medical fields.
Dentistry is more than a specialty of Medicine
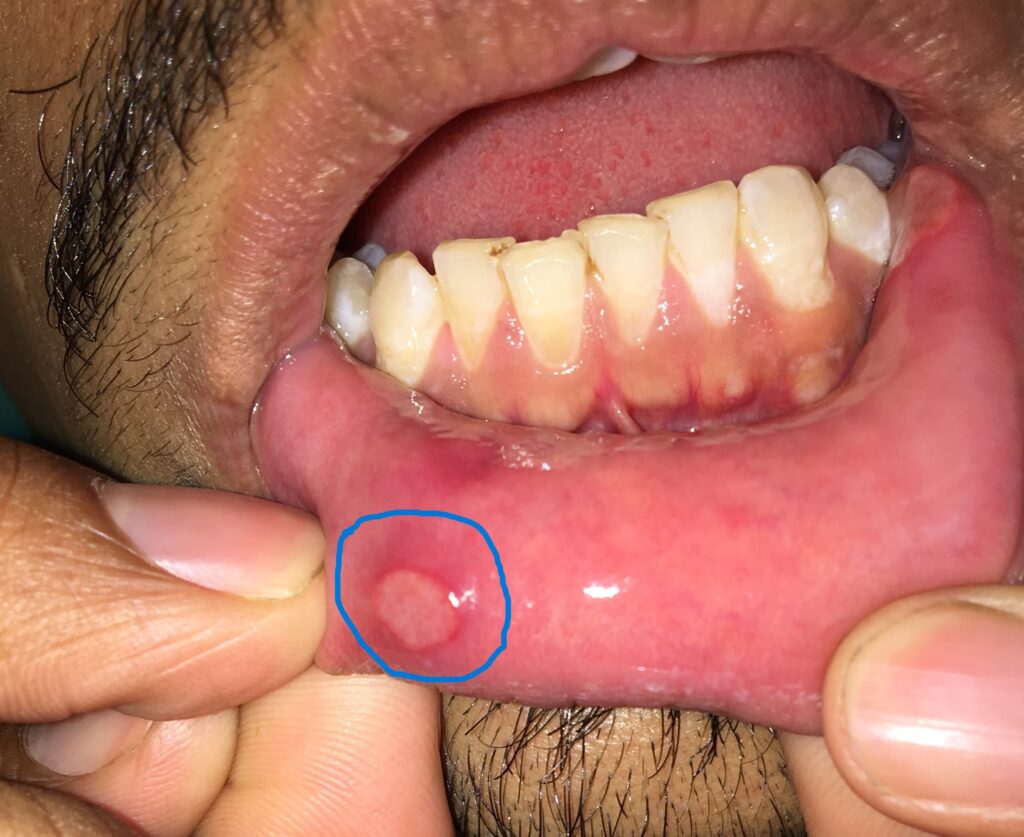
- Have you seen, everyone affected by cancer or diabetes, or heart problems? Have you seen a separate college for the liver or heart, in spite of the fact that we can’t live without these vital organs? Some people have skin problems; some have kidney issues but every one of us has dental problems and needs regular dental prophylaxis or treatments. The mouth is a constant source of microbial inflammation. Fortunately, most people are asymptomatic (painless) because we evolved and adapted to oral germs and constant inflammation. Just imagine, what would have happened if oral inflammation is painful in everyone.
- The mouth is the only natural way of food intake. It has the second largest diverse microbiota after the gut because of the easy availability of food and shelter. Furthermore, the modern refined(soft and sticky) diet has aggravated the situation and made our mouth the constant source of microbial inflammation. That’s why tooth decay and gum diseases are one of the most common diseases affecting mankind.
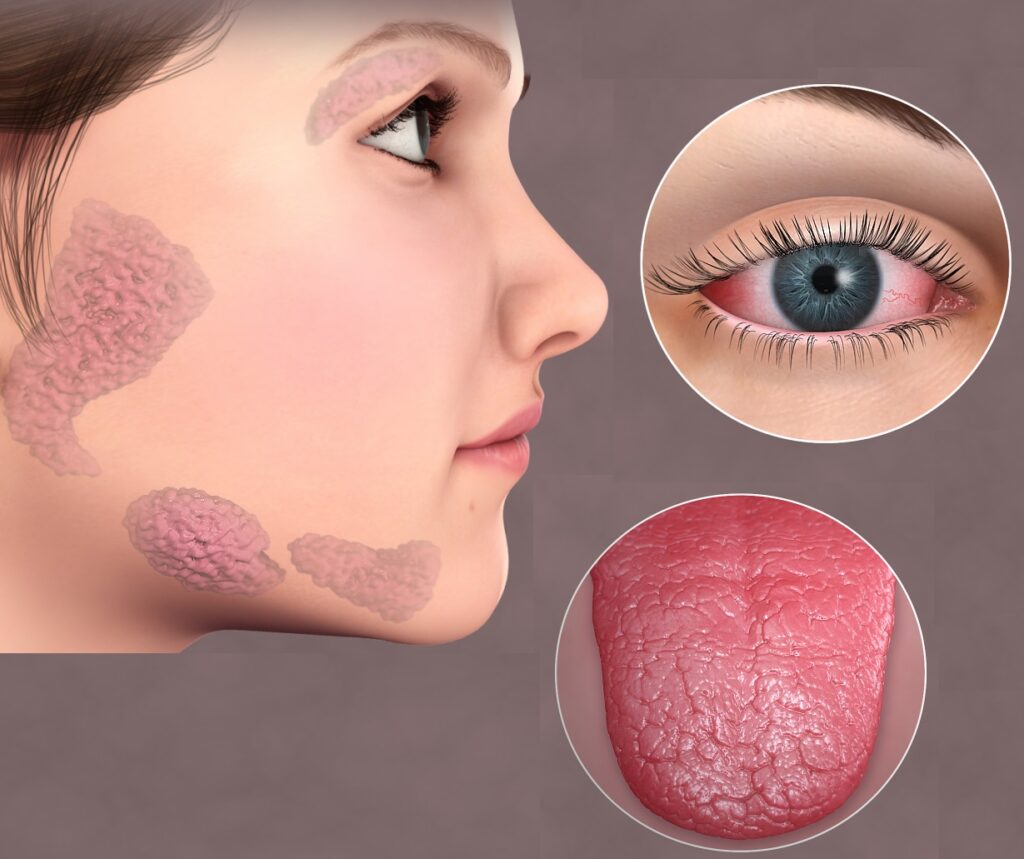
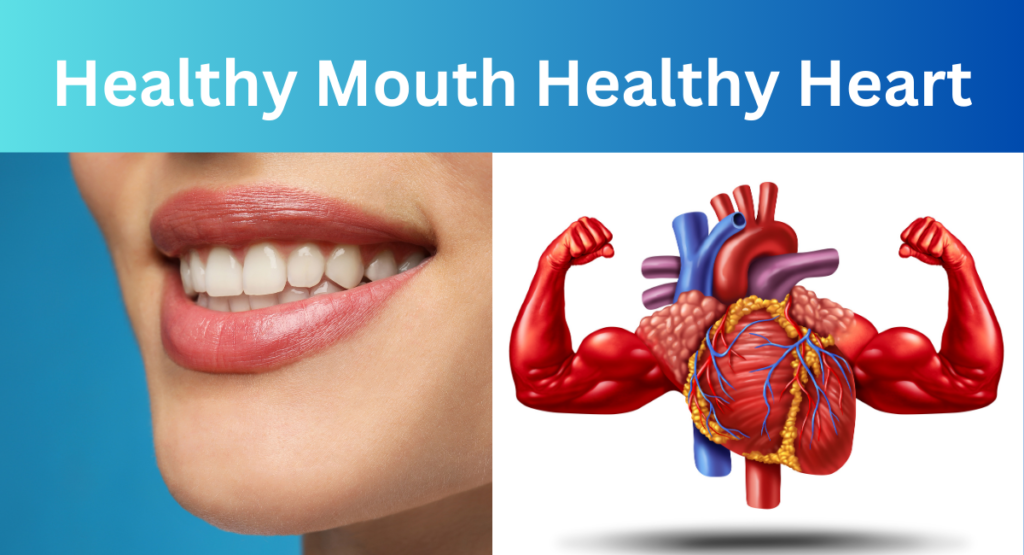
- Oral microflora, their toxins, and inflammatory products from mouth diseases get easy access to the inner body through our inflamed gums and can cause heart attacks, pneumonia, diabetes, cancers, infertility, sepsis, and many other ill-effects on our vital organs. Poor oral hygiene during pregnancy can affect the developing baby which can lead to complications such as miscarriage, low birth weight, and premature delivery. Poor oral health is not only linked with systemic diseases/conditions but badly influences their entire course. The mouth is the gateway to your systemic health.
- You must have noticed, the mouth is the only organ of your body that needs a variety of hygiene/preventive measures i.e., toothbrush, toothpaste, dental floss, tongue blade/brush, interdental brushes, mouthwashes, professional prophylaxis/treatments, etc. on a regular basis to maintain your oral as well as overall health.
- Most importantly, dental tissues once damaged cannot be regenerated or repaired by themselves, unlike other body cells. That’s why; Dentistry is not just a science but an art and engineering to rebuild lost tissues. Dentists have to be both doctors and engineers. Hence, Dentistry demands extensive, time-consuming, rigorous training to master its art and science. In Medicine, the prognosis of any disease depends on the doctor and patient. However, in dentistry, it depends on the doctor, the patient, and the bio-materials used to restore lost tissues.
- As everyone is a dental patient, dentists routinely encounter medically compromised patients (i.e., heart patients on blood thinner need dental extraction/cleaning). They have to be diagnosticians as well as surgeons. They have to manage anesthesia and its complications without the assistance of an Anesthetist. They also have to take and interpret X-rays without the assistance of a Radiologist. They have to be multifaceted.
- Furthermore, teeth, gums, jaws, salivary glands, and oral-facial structures are interconnected members of the same family. Therefore, to become a master in any one branch of dentistry, you require an additional three years of advanced training e.g., Endodontist (Restorative specialist), Periodontist (Gum specialist), Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeon (extraction and surgical management of oral-facial diseases), and so on.
- In medicine, 32 specialists for 1 patient, while in dentistry, 1 specialist for 32 patients (teeth). A set of 32 teeth plays a pivotal role, not only in maintaining oral-facial harmony but also in overall well-being.
Humans have two sets of teeth in their life:
- Primary (milk or deciduous) dentition comprises 10 teeth in each jaw (a total of 20 teeth).
- Permanent (adult) dentition comprises 16 teeth in each jaw (a total of 32 teeth).
Milk teeth play an essential role in the growth and development of jaws. They hold the spaces for permanent teeth to come in. Even if any one tooth is damaged, it affects the whole oral-facial ecosystem.
Conclusion
The modern refined (soft and sticky) sugary diet has made our mouth the constant source of microbial inflammation and worsened oral and systemic health. Therefore, every one of us is a dental patient. However, good oral health is necessary for an individual’s overall health and well-being. Teeth, gums, jaws, salivary glands, and oral-facial structures are interconnected members of the same family. You need special skills and knowledge to manage all. Furthermore, dental tissues once damaged cannot be regenerated or repaired by themselves. Dentists have to be both doctors and engineers. Hence, dentistry demands extensive, time-consuming, rigorous training to master its art and science. That’s why dentistry is more than a specialty of medicine. Please keep in mind, dentistry is not just limited to teeth.
FAQ
Ques – 1. What is dentistry?
Dentistry is a branch of medicine that deals with the prevention, diagnosis (detection), and treatment of diseases and conditions of teeth, gums, jaws, and oral-facial structures. Remember, the field of dentistry is not just limited to teeth.
Ques – 2. Why everyone has dental problems?
The modern refined (soft and sticky) sugary diet has made our mouth the constant source of microbial inflammation. The bacteria produce more acids from such refined sugary food and damage teeth structures. That’s why Tooth decay and gum diseases are one of the most common diseases affecting mankind.
Ques – 3. How oral health affects our overall health?
The mouth is a constant source of microbial inflammation. Oral microflora, their toxins, and inflammatory products from mouth diseases get easy entry into our inner body through dilated blood vessels of inflamed gums and can cause ill effects on vital organs resulting in systemic diseases.
Ques – 4. Can poor oral hygiene affect unborn babies?
Poor oral hygiene during pregnancy can affect not only your health but of developing baby. It can lead to complications such as miscarriage, low birth weight, and premature delivery. Poor oral health also increases the risk of infertility in both males and females.
Ques – 5. Which body parts cannot regenerate or repair after an injury?
Teeth are the only body parts that cannot regenerate or repair themselves.
Ques – 6. How many sets of teeth do humans have?
Humans get two complete sets of teeth over a lifetime:
- Primary (milk or deciduous) dentition comprises 10 teeth in each jaw (a total of 20 teeth).
- Permanent (adult) dentition comprises 16 teeth in each jaw (a total of 32 teeth).
Milk teeth are essential in the growth and development of jaws. Milk teeth do many important functions in children until they get their own complete set of permanent teeth to chew on.