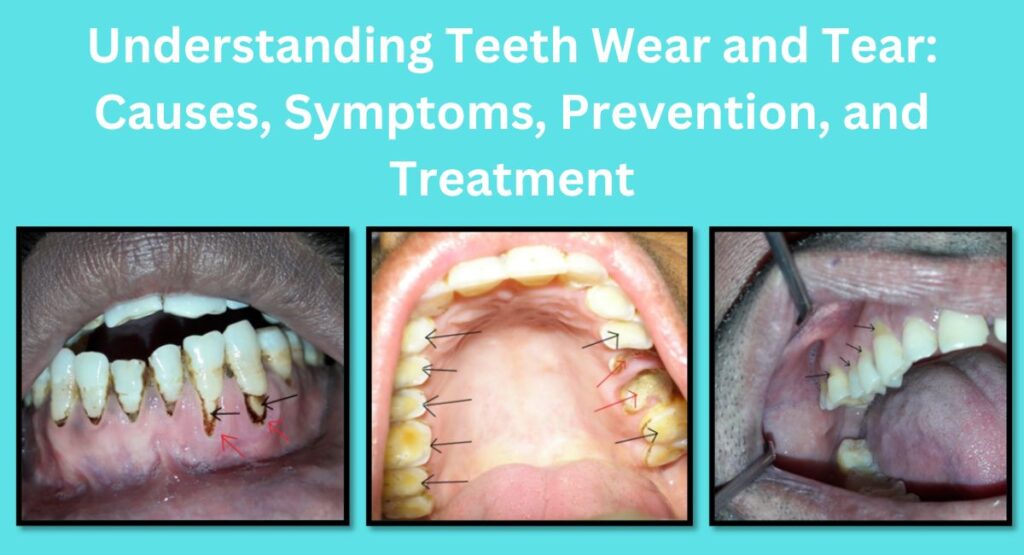
Teeth wear and tear
Teeth play a crucial role in our daily lives, aiding in chewing, speaking, and enhancing our facial aesthetics. However, over time, wear and tear on our teeth can occur, impacting their function and appearance. In this article, we will delve into what teeth wear and tear is, explore its different types, understand the causes, recognize symptoms, discuss preventive measures, and explore available treatments.
What is Teeth Wear and Tear?
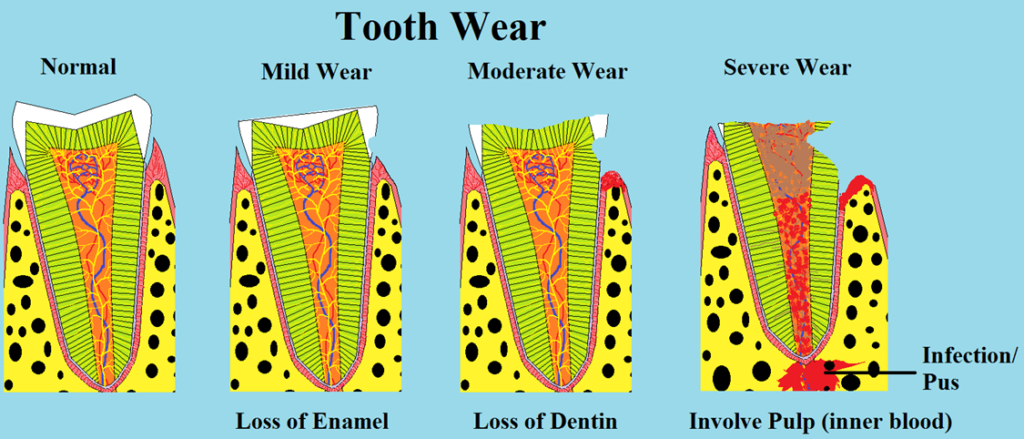
Teeth wear and tear refer to the gradual loss of tooth structure over time. This natural process can result from various factors and can affect the enamel, dentin, and even dental restorations like fillings and crowns.
Teeth wear and tear
Different Types of Teeth Wear
- Attrition: The wearing down of teeth due to grinding or clenching.
- Abrasion: External factors, such as aggressive tooth brushing, contribute to this type of wear.
- Erosion: Acidic substances, like sodas or citrus fruits, can lead to the loss of enamel.
- Abfraction: Microscopic fractures at the tooth’s neck caused by excessive force during biting or chewing.
Causes of Teeth Wear and Tear
Incorrect Brushing Technique: Brushing too hard or using a toothbrush with hard bristles can lead to abrasion.
Abrasive toothpaste: Regular use of abrasive toothpaste/powder (High RDA): Frequent use of toothpaste or powder with a high Relative Dentin Abrasivity (RDA) can contribute to teeth wear, gradually eroding enamel and causing long-term damage. Teeth cleaning powder is typically more abrasive than toothpaste, potentially leading to increased wear on enamel.
Poor Oral Hygiene: Inadequate brushing and flossing can lead to plaque buildup, causing wear.
Acidic Diet: Consuming acidic foods and drinks erodes enamel over time. Frequent consumption of sugary foods contributes to decay.
Teeth-whitening products: Regular use of tooth whitening or anti-tartar toothpaste: Repeated use of teeth-whitening chemicals, abrasive or bleaching agents in these products can contribute to teeth wear, potentially affecting enamel integrity over time.
Gastric/Eating disorders/heartburn: Chronic acid regurgitation, where stomach contents move into the mouth, can lead to teeth wear as the stomach acid dissolves the outer layer of teeth over time.
Bruxism (Teeth Grinding): Nighttime grinding or clenching can accelerate wear. Stress and anxiety contribute to bruxism.
Adverse habits/Professional damage: Nail biting, using teeth to open bottles, and holding objects like needles can contribute to teeth wear. Professions such as those in chemical factories, carpentry, tailoring, and painting may expose individuals to additional risks. Individuals in the fashion industry are more likely to experience anorexia nervosa, involving repeated vomiting due to a fear of gaining weight, which can contribute to dental erosion.
Misaligned teeth: Misaligned teeth distribute forces unevenly, resulting in wear (abfraction) at the neck of the tooth where the enamel is thin.
High oral frenums: A high oral frenum pulls the gums down, exposing weaker areas of teeth to irritants and causing wear. This indirectly contributes to the overall wear and tear of the teeth.
Symptoms of Teeth Wear and Tear
- Tooth Sensitivity: Increased sensitivity to hot, cold, or sweet stimuli.
- Changes in Teeth and Facial Appearance: Rounded edges or flattened surfaces. Yellowing or transparency due to enamel loss. Excessive wear on biting surfaces can result in overclosure of the mouth, leading to collapsed cheeks, reduced chewing efficiency, and aesthetic concerns that impact one’s personality.
- Gum Recession: Exposed tooth roots due to wear.
- Pain and Discomfort: Toothaches or jaw pain, especially while eating.
Prevention of Teeth Wear and Tear
Prevention is better than cure.” Keep in mind that teeth cannot repair themselves naturally.
- Choosing the Right Tools for Oral Care: Choose a soft-bristled toothbrush and low RDA (Relative Dentin Abrasivity) toothpaste to minimize abrasion. Use fluoride toothpaste to aid in the remineralization of worn-down parts of teeth.
- Maintain Good Oral Hygiene: Brush your teeth twice a day and floss regularly to prevent plaque buildup, using the correct brushing and flossing techniques.
- Limit Acidic Foods and Drinks: Refrain from consuming sodas and carbonated drinks. When enjoying acidic fruit juices, use a straw to minimize direct contact with teeth. Additionally, avoid direct consumption of acidic fruits. Follow up with plenty of water, and avoid brushing immediately after consuming acidic foods and drinks.
- Wear a Mouthguard: For those with bruxism, wearing a mouthguard at night can prevent excessive grinding.
- Healthcare Guidance for Digestive Concerns: Seek advice from your physician if you experience gastric reflux or suspect eating disorders. Consulting a healthcare professional can provide valuable insights and guidance regarding gastric reflux or potential eating disorders.
- Seek Professional Guidance: Consult with your dental surgeon or oral physician to identify potential causes and explore treatments for teeth clenching or grinding as a preventive measure.
Treatment Options for Teeth Wear and Tear
- Managing Incipient Tooth Wear: In incipient wear, where restoration may not be feasible, focus on preventive measures to avert further damage. Additionally, manage teeth sensitivity through targeted strategies to enhance oral comfort.
- Tooth-Colored Fillings: Composite fillings to repair cavities caused by wear.
- Dental Crowns: Caps are placed over severely worn teeth for both protection and restoration. In some cases, severely worn teeth may necessitate root canal treatments for comprehensive repair.
- Addressing Severe Tooth Wear: In cases of severely worn teeth, extraction may be necessary, followed by the replacement of artificial teeth for optimal oral function and aesthetics.
- Orthodontic Treatment: Correcting misaligned teeth to distribute forces evenly during biting.
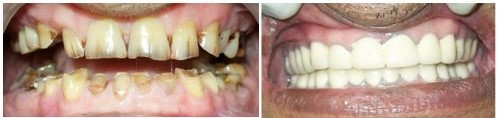
Treatment of Severely Worn Down Teeth
(Image Source: Courtesy of Dr. Sudhanshu Gupta)
Conclusion
Understanding teeth wear and tear is crucial for maintaining optimal oral health. By recognizing the causes, symptoms, and preventive measures, individuals can take proactive steps to preserve their teeth and prevent further damage. If wear has already occurred, various treatment options are available to restore and protect teeth, ensuring a healthy and confident smile for years to come.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Can teeth wear be reversed?
No, teeth wear cannot be reversed, but certain preventive measures and treatments can slow down further deterioration.
How can I prevent enamel erosion?
To prevent enamel erosion, limit the consumption of acidic foods and drinks, maintain good oral hygiene practices, and consider using fluoride treatments to strengthen the enamel.
Is teeth grinding treatable?
Yes, teeth grinding (bruxism) can be managed. Using a custom-made mouthguard, especially at night, helps reduce the impact of grinding. Additionally, stress reduction techniques and lifestyle changes may contribute to treatment.
Are there natural remedies for tooth sensitivity?
Desensitizing toothpaste containing potassium nitrate can help alleviate tooth sensitivity. Maintaining good oral hygiene, including gentle brushing and regular flossing, is also essential.
How often should I visit the dentist to monitor teeth wear and tear?
Regular dental check-ups are crucial for monitoring teeth wear and catching any issues early on. It is generally recommended to visit the dentist every six months, but your dentist may suggest a more personalized schedule based on your oral health needs.
Can poor nutrition contribute to teeth wear and tear?
Yes, a diet lacking essential nutrients, particularly calcium and phosphorus, can weaken teeth and contribute to wear and tear. Ensure a well-balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals to support overall oral health.
Are there lifestyle changes that can reduce teeth wear?
Avoiding habits like nail-biting, chewing on ice, or using teeth as tools can help minimize wear. Additionally, staying hydrated and maintaining a balanced diet contribute to overall oral health.
Can children experience teeth wear and tear?
Yes, children can experience wear and tear, especially if they grind their teeth (bruxism) or consume acidic foods and drinks. Supervising their oral hygiene routines, ensuring a balanced diet, and addressing any dental concerns early on are essential.
Is teeth wear and tear solely a result of aging?
While aging can contribute to wear and tear, it is not the sole factor. Lifestyle habits, oral hygiene practices, and underlying conditions can also play a significant role. Taking preventive measures throughout life is crucial for maintaining healthy teeth.
Can stress contribute to teeth wear?
Yes, stress can contribute to teeth wear, particularly through the habit of teeth grinding (bruxism). Managing stress through relaxation techniques and, if necessary, seeking professional guidance can help alleviate its impact on oral health.